10 Best Industrial Robots for Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency?
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, the role of industrial robots is more vital than ever. Experts like Dr. Emily Carter, a prominent figure in robotics, emphasize, "The future of production lies in intelligent automation." As industries strive to enhance productivity and efficiency, the integration of industrial robots represents a significant shift. These machines streamline processes, reduce human error, and improve output quality.
Yet, the journey is not without challenges. Selecting the right industrial robot can be daunting. Each model comes with unique capabilities and limitations. Businesses must reflect on their specific needs before investing. Often, companies underestimate the training required for effective robot integration.
Moreover, while industrial robots promise efficiency, they also spark debates about job displacement. It’s essential to balance automation with workforce development. Organizations must consider how to upskill employees alongside adopting new technologies. This dual approach is key to navigating the evolving industrial landscape effectively.

Overview of Industrial Robots and Their Role in Manufacturing
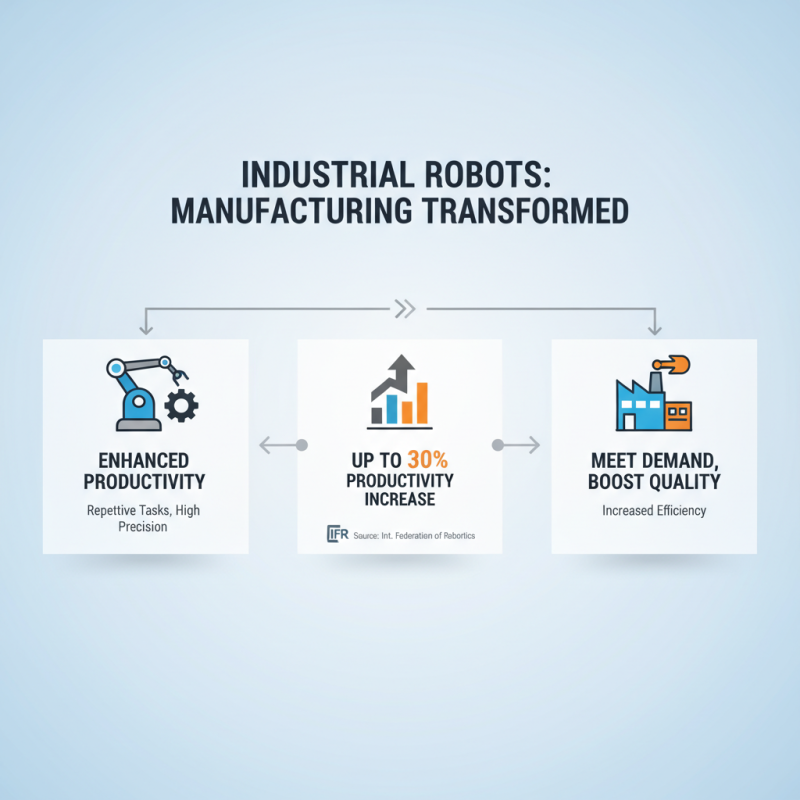
Industrial robots have transformed manufacturing processes significantly. They enhance productivity by performing repetitive tasks with high precision. According to a recent data report by the International Federation of Robotics, companies that utilize industrial robots may see a productivity increase of up to 30%. This increased efficiency allows businesses to meet higher demand without compromising quality.
However, the integration of robots also presents challenges. For instance, they require significant initial investment and specialized training for staff. Many manufacturers struggle with the transition phase. A survey by McKinsey revealed that 70% of companies faced obstacles in fully implementing automation. The human element remains crucial, as workers often need to adapt to new roles alongside robotic systems.
Moreover, while robots can execute tasks flawlessly, they lack the flexibility of human workers. For example, they often struggle with complex problem-solving scenarios. Companies must evaluate whether the benefits outweigh the potential downsides. It’s critical to approach robot integration thoughtfully, addressing both technological and human factors for optimal outcomes.
Criteria for Selecting the Best Industrial Robots for Productivity
When selecting industrial robots, focus on key criteria to ensure enhanced productivity. Assess the robot's payload capacity. It should match your operational needs. Consider the robot's reach and flexibility. A versatile robot adapts to various tasks easily. Speed is another important factor. Efficient robots can significantly reduce cycle times.
**Tip:** Always plan for future upgrades. Technology changes swiftly. Opt for robots with modular designs. These allow easy adaptations to your evolving processes. Another critical aspect is the software compatibility. Robust software ensures seamless integration with existing systems.
Moreover, don't overlook the ease of training operators. Some robots require extensive training, which can stall productivity. A user-friendly interface is valuable. It reduces training time and improves efficiency. Lastly, think about maintenance and support. Regular upkeep can prevent unexpected downtimes. However, not every robot is easy to maintain. Make sure to investigate this before purchase.
Top 10 Industrial Robots: Specifications and Features
Industrial robots have revolutionized manufacturing. They enhance productivity, but not every robot fits every task. Understanding specifications and features is crucial for selecting the right one.
Robots vary in payload capacity, reach, and precision. Some excel in welding, while others are better for assembly. Speed is another factor. A faster robot can boost output, but it may compromise accuracy. Data shows that choosing the right spec can minimize downtime.
Connectivity is vital too. Many robots now integrate with IoT systems. This allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments. However, not all facilities are ready for such technology. Upgrading can be costly and complex. Continuous training for staff remains a challenge. Balancing advanced machines with a skilled workforce is key to maximizing efficiency.
Top 10 Industrial Robots: Productivity and Efficiency Metrics
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Industrial Robots
In recent years, many industries have embraced automation. Successful implementation of industrial robots demonstrates this trend. In one case, a manufacturing plant integrated robotic arms for assembly tasks. Productivity soared, but workers felt anxious about job security. Training programs emerged, helping employees adapt.
Another example comes from a food processing company. They deployed robots for packaging and palletizing. The robots handled heavy loads swiftly and reduced waste. However, downtime due to maintenance issues occasionally disrupted production. Staff needed to examine workflows to enhance efficiency further.
These cases show mixed results. While robots boost productivity, they also create challenges. Companies must balance technology with human roles. Reflection on employee experiences is vital. Continuous improvement is essential in this evolving landscape.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation and Robotics Technology
The future of industrial automation and robotics is bright but complex. According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, by 2025, the global stock of industrial robots may reach 20 million units. This growth represents a significant shift in production processes across various industries. However, the transition is not without its challenges. Many companies struggle with integration, skills gaps, and high initial investments.
Data from McKinsey & Company suggests that automation can increase productivity by up to 30%. Yet, many businesses remain hesitant. Training employees to operate and manage these advanced systems is crucial. The World Economic Forum estimates that 85 million jobs may be displaced by automation by 2025, while 97 million new roles could emerge. This represents a critical moment for the workforce to adapt.
Moreover, companies are increasingly focusing on collaborative robots, or cobots. These machines work alongside human operators, enhancing safety and flexibility. Yet, there is a need for more robust safety standards. As industries evolve, manufacturers must consider the potential for machine malfunctions and cyber threats. The path forward in robotics requires continuous evaluation and adaptation to harness full productivity potential.
Related Posts
-
Why Industrial Robots Are Essential for Modern Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Exploring Industrial Robot Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Digital Tips for Harnessing the Power of Robotic Automation Solutions
-

10 Essential Tips for Implementing Robotic Automation Effectively?
-
Exploring the Future of Robotic Manufacturing at China's 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

Exploring the Future: How Robotic Automation is Revolutionizing Everyday Tasks and Industries