How to Improve Your Robotic Welding Techniques for Better Results
The field of robotic welding has seen substantial advancements over the past decade, transforming the manufacturing landscape with enhanced precision, efficiency, and consistency. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, robotic welding solutions account for over 30% of applications in industrial robots, highlighting their growing significance across multiple industries including automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. With a projected market growth rate of 8.5% annually, it is more important than ever for companies to refine their robotic welding techniques to remain competitive.
Expert insights underscore the importance of continuously improving these techniques. Dr. Jane Foster, a leading authority in robotic automation, states, "The integration of advanced programming and quality control measures is essential for maximizing the performance of robotic welding systems." Her assertion emphasizes that the combination of technological advancements and skilled operation can lead to superior welding outcomes, reducing defects and increasing production speed. As companies increasingly adopt these sophisticated systems, understanding how to leverage their capabilities effectively will be vital for achieving better results in robotic welding.

Understanding the Basics of Robotic Welding Techniques
Robotic welding has become an essential component of modern manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency that manual welding often cannot achieve. Understanding the basics of robotic welding techniques is crucial for enhancing performance and achieving superior results. Key to this understanding is recognizing the different types of welding processes utilized in robotics, such as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. According to a recent industry report by the International Federation of Robotics, 72% of robotic applications in manufacturing are dedicated to welding, highlighting its critical role in production efficiency.
One vital concept in robotic welding is the programming of welding parameters, which directly affect weld quality. Variables such as travel speed, arc length, and welding voltage need to be meticulously set and calibrated according to the material being welded. This not only ensures a strong fusion between metals but also minimizes defects and reduces rework rates. Research indicates that optimizing these settings can lead to an up to 30% improvement in weld quality. Furthermore, advancements in sensor technology allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments during the welding process, enhancing adaptability and precision.
Additionally, correct positioning and calibration of the robotic arm are pivotal for achieving consistent results. Studies have shown that even minor deviations in positioning can lead to significant defects in the weld joint, resulting in structural weaknesses. Training personnel on the fundamentals of robotic welding, including maintenance and regular inspections, contributes to longer equipment lifespans and improved output quality. With the right techniques and understanding, manufacturers can leverage robotic welding to elevate their production capabilities to unprecedented levels.
Key Factors Influencing Robotic Welding Quality
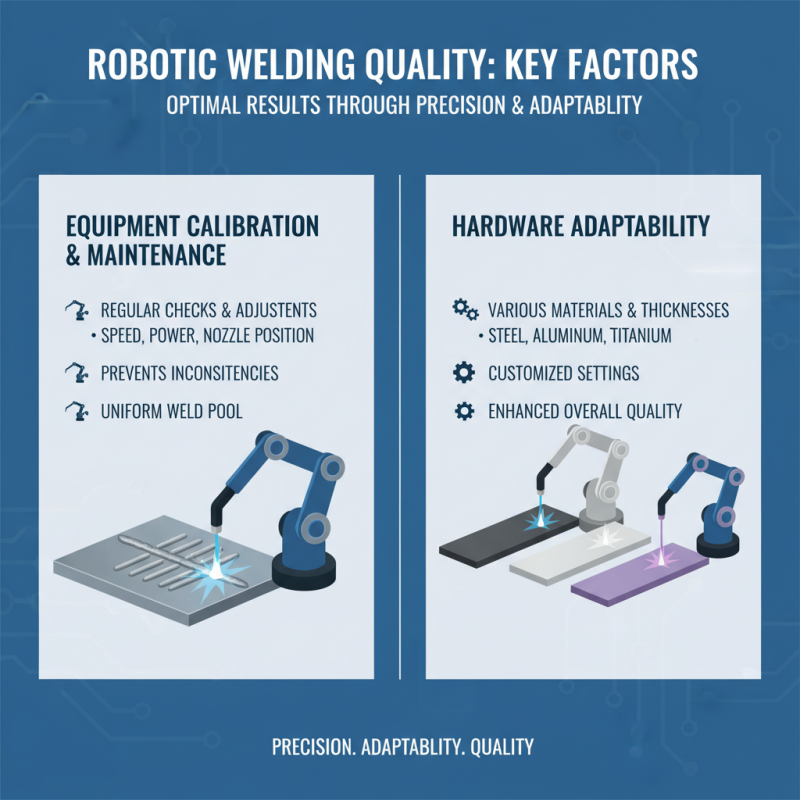
Robotic welding quality is significantly influenced by several key factors that require careful consideration to achieve optimal results. One of the primary determinants is the calibration and maintenance of the welding equipment. Regular checks and adjustments to the robot's parameters, including speed, power settings, and nozzle positions, can prevent inconsistencies and ensure a uniform weld pool. Additionally, the hardware's ability to adapt to various materials and thicknesses is crucial; customizing settings for different jobs enhances the overall quality of the welds produced.
Another critical factor is the programming of the robotic welding system. Well-structured programs that account for the geometry of the workpieces can drastically improve the precision and accuracy of the welds. Utilizing simulation software can help identify potential issues before production, ultimately saving time and resources. Operator expertise also plays a vital role, as skilled technicians can optimize the setup and troubleshoot problems during the welding process, leading to higher-quality outcomes. By focusing on these aspects, manufacturers can significantly enhance their robotic welding techniques and improve the reliability of their welds.
Common Challenges in Robotic Welding and Their Solutions
Robotic welding is an advanced manufacturing process that, while efficient, comes with its own set of challenges. One common issue is poor joint quality, which can result from improper alignment or inconsistent weld parameters. To address this, ensure that your workpieces are accurately positioned before the welding process begins. Regularly calibrating the robot’s sensors and settings can help maintain precision and improve weld integrity.
Another challenge in robotic welding is the difficulty in achieving proper heat control, leading to defects like warping or excessive spatter. To mitigate this, consider adjusting the welding speed and voltage settings to find an optimal balance that works for your specific application. Additionally, maintaining a clean environment around the welding area can prevent contamination, which often contributes to thermal inconsistencies.
Tips: Regular maintenance of your robotic equipment can greatly reduce downtime and enhance performance. Conduct routine inspections to identify any wear and tear on components. Furthermore, training operators on troubleshooting common issues can empower them to respond quickly, minimizing disruptions in the welding workflow. Remember, a proactive approach to addressing these challenges can lead to superior results in your robotic welding operations.
Advanced Technologies to Enhance Robotic Welding Performance
Advanced technologies are transforming the landscape of robotic welding, enabling manufacturers to achieve superior quality and efficiency. One of the key advancements is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can analyze welding processes in real-time, identifying inconsistencies and optimizing parameters automatically. This leads to precise control over heat and speed, ultimately enhancing joint integrity and minimizing defects.
Another notable innovation is the use of advanced sensors and vision systems. These technologies allow robotic welders to "see" the welding area, adjust dynamically to variations in joint fit-up, and ensure accurate application of welding materials. By incorporating depth perception and imaging, welders can improve alignment and penetration, which boosts the strength of welds significantly.
Tips: To harness these technologies effectively, ensure that your team is trained on operational software and understands the significance of routine calibrations. Regular updates to algorithms in AI systems can also help maintain optimal performance. Additionally, integrating feedback loops from sensors can provide invaluable data for continuous improvement, helping welders refine their techniques further.
Enhancing Robotic Welding Techniques
This chart illustrates the impact of integrating advanced technologies on robotic welding performance across various parameters. It highlights the percentage improvement in welding speed, precision, and quality after implementing these technologies.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Calibration of Welding Robots
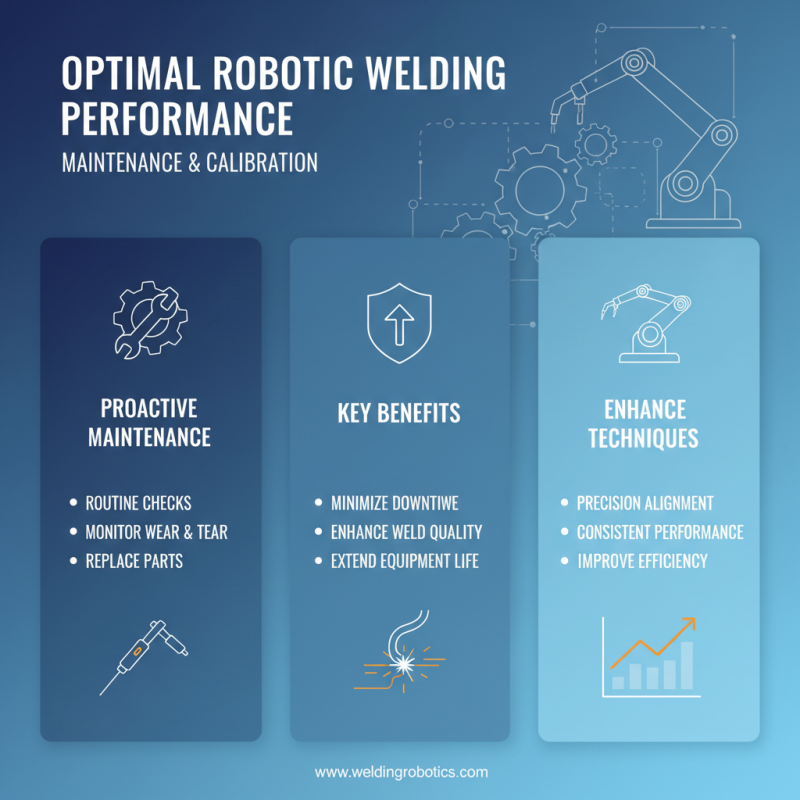
Proper maintenance and calibration of welding robots are essential for achieving optimal performance and improving your robotic welding techniques. Regular maintenance ensures that all components function efficiently, minimizing downtime and enhancing the quality of welds. A proactive approach to maintenance involves routine checks on the welding equipment, including the power source, torches, and wire feed mechanisms. Monitoring wear and tear, and replacing parts as necessary, can prevent unexpected failures that disrupt production.
**Tips:** Schedule weekly maintenance checks to assess the condition of your welding robots. Keep a log of all maintenance activities and any issues encountered to spot patterns that may indicate the need for further scrutiny. Additionally, ensure that the workspace is free from debris and hazardous materials that could interfere with the robots’ operation.
Calibration is another critical aspect of ensuring the precision and reliability of robotic welding. Regularly calibrate the welding parameters such as voltage, wire feed speed, and travel speed according to the specifications of the materials being joined. This helps maintain consistent weld quality and minimizes the risk of defects.
**Tips:** Use a checklist for calibration procedures to ensure no steps are overlooked. Involve your team in the calibration process, as their insights can help identify deviations in performance that may require attention. Keeping calibration records can also assist in tracking any variances and guide improvements in your welding processes.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Future of Robotic Welding in Industry 4.0
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing with Robotic Welding Machines for Enhanced Efficiency
-

2025 Top 10 Robotic Welding Systems Revolutionizing Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Top 10 Tips for Mastering Robotic Spot Welding Techniques
-

What is Robotic Welding Solutions? Exploring Automation in the Welding Industry with Data Insights
-

5 Automation System Tips to Boost Operational Efficiency by 30 Percent